Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Among its many complications, diabetic foot ulcers and wounds are particularly concerning. These wounds, often resulting from neuropathy, poor circulation, or a weakened immune system, can lead to severe infections, amputations, and even mortality if not managed effectively. Early intervention in diabetic wound care is critical to improving outcomes, reducing complications, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds, particularly foot ulcers, are a common complication for people with diabetes. Peripheral neuropathy often diminishes the sensation in the feet, making it difficult for individuals to detect minor injuries or pressure sores. Poor circulation caused by diabetic vascular disease can impede the healing process, making even small wounds prone to infections.
These wounds often develop in stages. A small, seemingly harmless blister or cut can quickly progress into a deep ulcer if left untreated. This progression underscores the importance of addressing wounds promptly and effectively to prevent them from reaching advanced stages.
The Risks of Delayed Treatment
Delays in treating diabetic wounds can have dire consequences. Here are some of the most significant risks:
- Infections: Diabetic wounds are highly susceptible to bacterial infections. Without timely care, infections can spread to the surrounding tissue or even enter the bloodstream, causing sepsis.
- Amputation: Advanced wounds that fail to heal or become severely infected may require amputation. According to the American Diabetes Association, nearly 85% of diabetes-related amputations begin with a foot ulcer.
- Chronic Pain and Disability: Unresolved wounds can lead to chronic pain and limit mobility, drastically affecting a person’s quality of life.
- Financial Burden: The cost of treating advanced diabetic wounds is significantly higher than addressing them in the early stages. Hospitalizations, surgeries, and long-term care can impose substantial financial burdens on individuals and healthcare systems.
Benefits of Early Intervention
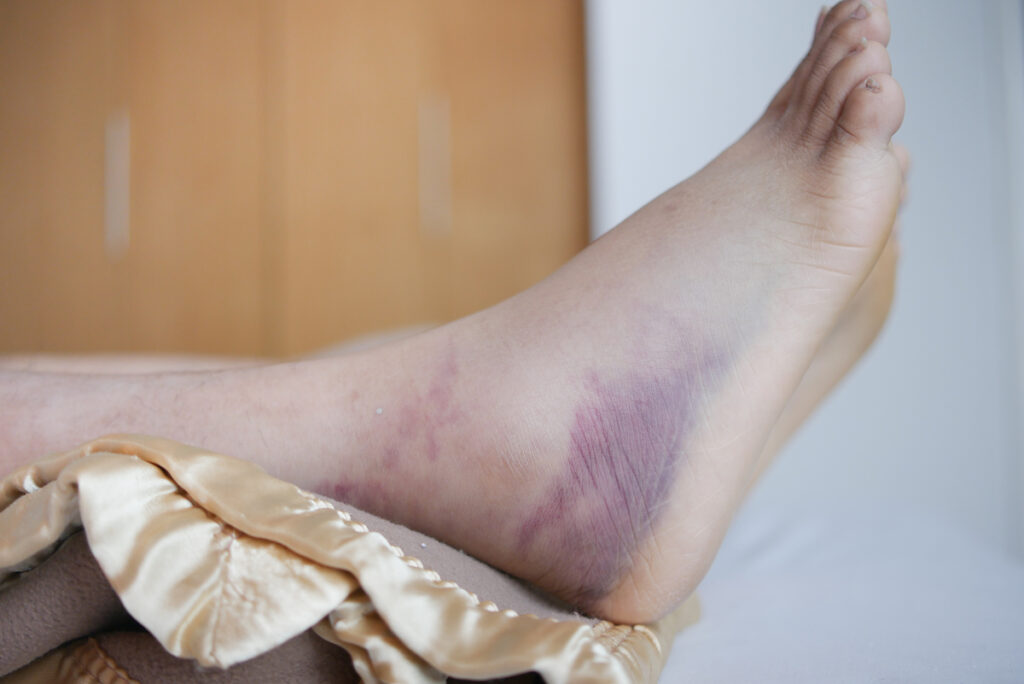 Early intervention in diabetic wound care offers several advantages that can prevent complications and promote healing:
Early intervention in diabetic wound care offers several advantages that can prevent complications and promote healing:
1. Improved Healing Outcomes
Addressing wounds at an early stage facilitates faster healing. Proper wound cleaning, debridement, and application of dressings can prevent infection and promote tissue regeneration. Early care minimizes the risk of wounds becoming chronic or progressing to severe infections.
2. Reduced Risk of Amputation
When wounds are identified and treated promptly, the likelihood of amputation decreases significantly. Regular monitoring and immediate action can stop infections and tissue damage before they become irreversible.
3. Lower Healthcare Costs
Timely treatment is cost-effective. Preventing the progression of wounds reduces the need for expensive interventions like surgeries, prolonged hospital stays, and rehabilitation services.
4. Enhanced Quality of Life
Managing wounds early allows individuals to maintain mobility, reduce pain, and avoid the psychological distress associated with severe complications. Early intervention empowers individuals to live more independently and actively.
Strategies for Early Intervention
Effective early intervention in diabetic wound care requires a multifaceted approach that includes prevention, early detection, and comprehensive treatment.
1. Regular Foot Inspections
Daily foot checks are essential for people with diabetes. They should look for signs of redness, swelling, blisters, cuts, or changes in skin texture. Caregivers and healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of this routine.
2. Preventive Foot Care
Wearing proper footwear, keeping feet clean and moisturized, and avoiding walking barefoot can prevent injuries. Regular visits to a podiatrist for toenail care and callus removal can also reduce risks.
3. Education and Awareness
Education is a cornerstone of early intervention. Individuals with diabetes should be informed about the risks of wounds, the importance of blood sugar control, and the need for prompt medical attention for any foot abnormalities.
4. Multidisciplinary Care
A collaborative approach involving endocrinologists, podiatrists, wound care specialists, and nutritionists ensures comprehensive care. Each specialist plays a vital role in addressing the multifactorial nature of diabetic wounds.
5. Advanced Wound Care Techniques
Modern wound care technologies, such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, bioengineered skin substitutes, and negative pressure wound therapy, can expedite healing when applied early. These treatments are most effective when wounds are managed promptly.
6. Blood Sugar Management
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is critical to wound healing. High glucose levels impair immune function and delay tissue repair. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve glycemic control.
7. Prompt Medical Attention
Any sign of a wound, no matter how minor, should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare provider. Early professional evaluation can prevent minor issues from escalating.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in promoting early intervention. Regular check-ups should include foot examinations, particularly for patients with a history of ulcers or neuropathy. Providers should educate patients on the importance of wound care and provide clear instructions on what to do if a wound is detected.
Healthcare systems can also adopt strategies to improve access to care, such as:
- Establishing specialized diabetic wound care clinics.
- Utilizing telemedicine to provide guidance and support to patients in remote areas.
- Training primary care providers to recognize and manage early-stage diabetic wounds.
Overcoming Barriers to Early Intervention
Despite the benefits of early intervention, several barriers can impede timely care. These include:
- Lack of Awareness: Many individuals underestimate the seriousness of diabetic wounds and delay seeking care.
- Access to Care: Limited access to healthcare facilities or specialists can delay treatment, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
- Financial Constraints: The cost of medical visits, dressings, and advanced treatments may deter individuals from seeking care.
- Psychological Factors: Fear, denial, or depression can prevent individuals from addressing wounds promptly.
Addressing these barriers requires public health initiatives, community outreach programs, and policies that enhance access to affordable and timely care.
The importance of early intervention in diabetic wound care cannot be overstated. Prompt and effective management can prevent complications, reduce healthcare costs, and improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Through education, preventive measures, and access to specialized care, healthcare providers and patients can work together to mitigate the risks associated with diabetic wounds. Recognizing the urgency of early intervention and acting swiftly can make the difference between healing and severe complications—or even life and death.
Looking for a Reliable Podiatrist in New Jersey?
Dr. Manooj Prasad at Garden State Foot & Ankle Group of Toms River is a highly experienced podiatrist with an ardent mission to help those suffering from foot, ankle, and lower leg issues. He offers personalized care while considering each patient’s lifestyle needs so that the best possible treatment can be administered. Based in both Essex County and Ocean County in New Jersey, service towns include Toms River, Livingston, Millburn, Short Hills, Lakewood, Ocean Gate, Lakehurst, Montclair, Jackson, Belleville, Roseland, Point Pleasant, Cedar Grove, and many more! For more information, you can contact us today at (732)557-9900 (Toms River) or 973)450-3035 (Belleville) or explore our website.
0 Comments