Stress fractures in feet are a common yet often misunderstood injury, especially among athletes, runners, and individuals with physically demanding routines. Unlike complete bone breaks that happen suddenly, stress fractures develop gradually due to repetitive force or overuse. These tiny cracks in the bone may seem minor at first, but without proper treatment, they can evolve into more serious problems, potentially requiring long-term recovery.
At Garden State Foot & Ankle Group, we understand the importance of early detection and specialized care when it comes to stress fractures in feet. Our team of foot and ankle experts uses advanced diagnostics and personalized treatment strategies to help patients return to pain-free activity as quickly and safely as possible. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what causes stress fractures, the warning signs to look out for, and the latest approaches to treatment and prevention.
What Are Stress Fractures in Feet?
Stress fractures in feet are small cracks or severe bruising within a bone, typically caused by repetitive motion or increased load. These fractures are most commonly seen in the metatarsal bones, which are responsible for supporting weight and movement during walking, running, or jumping. While stress fractures can affect anyone, they are especially common among athletes, military personnel, and individuals who suddenly increase their physical activity without adequate preparation.
The bones in your feet endure significant stress each day. When this stress exceeds the bone’s ability to repair and regenerate, tiny cracks may form. These micro-injuries can accumulate over time, eventually developing into a stress fracture. The condition is frequently linked to overtraining, improper footwear, or underlying conditions such as osteoporosis, which weakens bone density. Women are also at greater risk, particularly those with low bone mass or menstrual irregularities.
If left untreated, stress fractures in feet can worsen, leading to a full break that may require immobilization, surgery, or a prolonged absence from physical activity. That’s why understanding the early signs and causes is essential for prompt and effective treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of a Stress Fracture
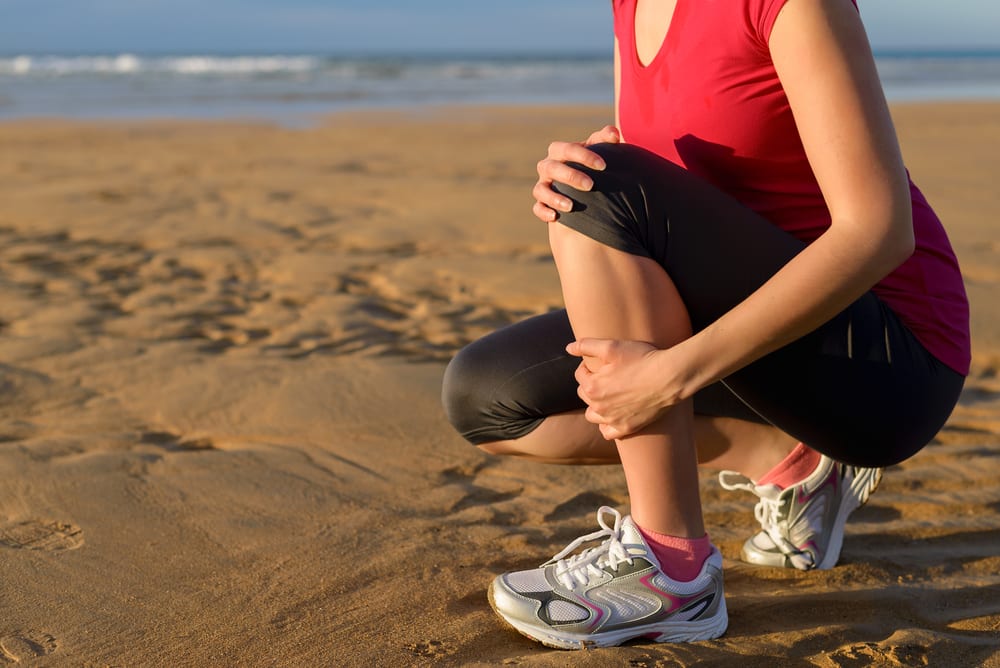
The symptoms of stress fractures in feet can be subtle at first, making them easy to overlook or misattribute to muscle soreness. However, the discomfort usually becomes more specific and persistent over time. Most patients describe a dull, aching pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest. As the injury progresses, the pain may become sharper and more localized.
You may also experience swelling over the top of the foot, tenderness to the touch, and bruising. Some people notice a slight limp or change in gait, as the body attempts to offload pressure from the affected area. It’s important not to ignore these signs, especially if the pain continues for more than a few days or intensifies during regular activity.
In particular, watch for:
- Pain that worsens with walking, running, or jumping and improves with rest: This pain often begins as a mild ache and becomes sharper over time. Continuing activity can exacerbate the fracture.
- Swelling, especially near the site of the fracture: The foot may appear puffy or inflamed, making it difficult to wear shoes comfortably. Swelling usually becomes more noticeable by the end of the day.
- Tenderness that increases when pressure is applied directly over a bone: This localized sensitivity can help pinpoint the exact area of the stress fracture. The pain is often easy to reproduce during a physical exam.
- A visible bump or bruising on the top or side of the foot: Discoloration or a raised area may develop as inflammation progresses. These signs often accompany swelling and tenderness.
- Decreased performance or reluctance to bear weight: You might find yourself avoiding certain movements or compensating with the opposite foot. This change in gait can lead to additional injuries if not addressed.
If you suspect a stress fracture, it’s best to stop physical activity immediately and consult a podiatrist. Delaying treatment can lead to more complex injuries and longer recovery times.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are multiple factors that contribute to the development of stress fractures in feet. Repetitive impact on hard surfaces is a primary cause, especially in high-impact sports like running, basketball, and tennis. Training errors such as increasing intensity or mileage too quickly can also place too much strain on bones that haven’t had time to adapt.
Other risk factors include wearing worn-out or unsupportive shoes, having poor foot mechanics such as flat feet or high arches, and engaging in activities without proper warm-up and cooldown routines. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in calcium and vitamin D, can also weaken bone strength and make fractures more likely.
Medical conditions such as osteoporosis, arthritis, or eating disorders further increase the likelihood of stress fractures. Women with the female athlete triad — a combination of disordered eating, irregular menstruation, and low bone density — are particularly vulnerable. Understanding your personal risk factors can help you take proactive steps to prevent injury.
Diagnosing Stress Fractures in Feet
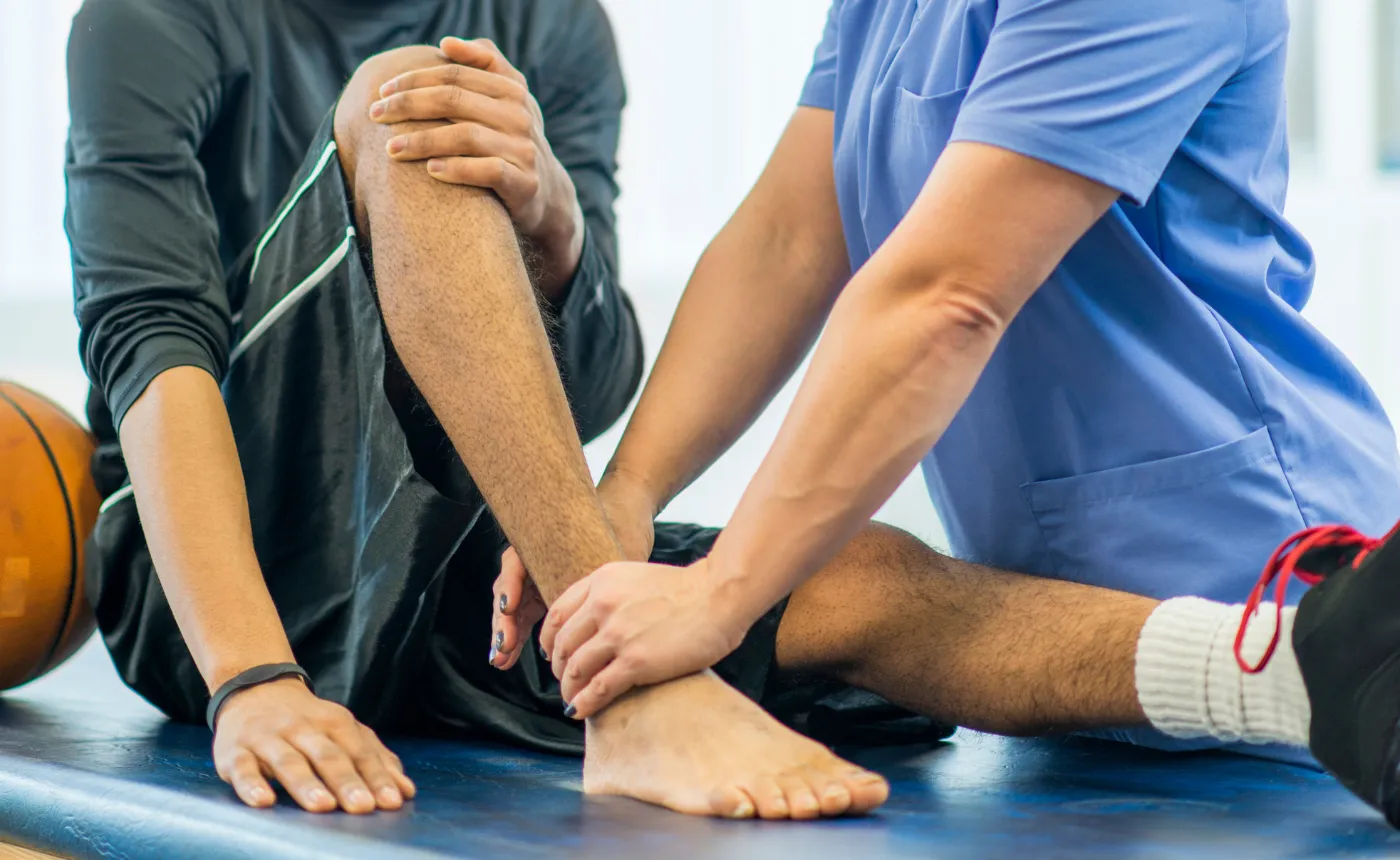
Proper diagnosis of stress fractures in feet involves a thorough physical exam and a detailed discussion of your symptoms and activity level. Your podiatrist will palpate the foot to identify areas of tenderness and evaluate your gait for signs of compensation. In many cases, a stress fracture may not appear on a standard X-ray during the early stages, so additional imaging tests may be necessary.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or bone scans offer more accurate results for detecting early-stage fractures. These advanced diagnostics help determine the exact location, severity, and stage of healing — all of which are important in formulating the right treatment plan.
Accurate diagnosis is key to avoiding further injury and beginning an appropriate course of treatment. At Garden State Foot & Ankle Group, we prioritize timely evaluations and patient education, so you understand the nature of your condition and the options available for healing.
Treatment Options for Stress Fractures
Treating stress fractures in feet typically begins with conservative methods designed to reduce strain on the affected area and allow the bone to heal. The most important component is rest. Depending on the location and severity of the fracture, your podiatrist may recommend avoiding all weight-bearing activities for several weeks.
Other common treatments include:
- Protective Footwear or Boots: These reduce impact and protect the bone while it heals. They help immobilize the foot and promote optimal alignment during recovery. Your podiatrist may recommend a walking boot for moderate to severe cases.
- Crutches or Mobility Devices: Used to keep weight off the injured foot entirely. This helps prevent further injury and gives the fracture time to mend. Knee scooters may be more comfortable for longer recovery periods.
- Ice Therapy and Elevation: Helps reduce swelling and control pain. Applying ice for 15–20 minutes several times a day can speed up recovery. Keeping the foot elevated above heart level minimizes fluid buildup.
- Medication: NSAIDs like ibuprofen can help manage pain and inflammation. Always consult your doctor before taking medication regularly, especially if you have other health concerns.
- Activity Modification: Switching to low-impact activities like swimming or cycling during recovery. These alternatives allow you to maintain cardiovascular fitness without compromising the healing process. Gradual reintroduction to high-impact activities is key.
In rare cases where the fracture does not heal properly, surgery may be required to stabilize the bone. This is more likely in high-risk areas like the fifth metatarsal. Regular follow-ups are essential to track progress and ensure a safe return to activity.
Preventing Stress Fractures
Preventing stress fractures in feet begins with a balanced approach to activity and rest. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of exercise allows bones to adapt to increased loads. Cross-training with low-impact activities can help reduce repetitive stress while maintaining fitness.
Proper footwear is essential. Choose shoes that provide adequate arch support, cushioning, and stability for your specific foot type and activity. Replace worn-out shoes regularly, as deteriorated soles and insoles no longer provide effective protection.
Nutrition also plays a critical role. A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein supports bone health. If you are at risk for nutritional deficiencies, consider supplements as advised by your doctor. Additionally, listening to your body and resting at the first sign of discomfort can prevent minor issues from becoming serious injuries.
Get Expert Care at Garden State Foot & Ankle Group
If you’re dealing with persistent foot pain or suspect a stress fracture, early diagnosis and personalized treatment are the keys to a full recovery. At Garden State Foot & Ankle Group, our experienced team is committed to helping you heal quickly and return to the activities you love. We provide expert care for stress fractures in feet, offering advanced imaging, individualized treatment plans, and preventative guidance tailored to your lifestyle.
Whether you’re an athlete or someone who simply spends a lot of time on your feet, don’t let pain slow you down. Contact us today for a thorough evaluation and take the first step toward healing with confidence.
Contact Garden State Foot & Ankle Group
Toms River Office
📍 664 Commons Way Building 1
Toms River, NJ 08755
📞 Phone: (732) 557-9900
📧 Email: gsfagroup@gmail.com
Belleville Office
📍 1 Clara Maas Drive
Belleville, NJ 07109
📞 Phone: (973) 450-3035
🌐 Website: gsfagroup.com


0 Comments